
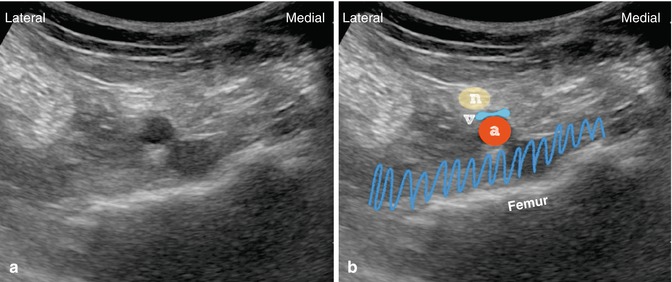
Despite this transition, only a small fraction of patients achieved the ability to dangle and participate with physical therapy on POD#0.įigure 2: iPACK block with local anesthetic deposited between the femur and the popliteal artery in an out-of-plane approach. However, to facilitate early physical therapy, the nerve catheter was frequently discontinued on POD#1 following multidisciplinary consultations with orthopedicsĪnd physical therapy. Initially, the femoral nerve blockĬatheters remained in place until day 2 (POD#2) to extend the duration of analgesia. The nerve block catheters were infused with a solution of 0.1% bupivacaine at a rate of 6 mL/hr with a 4 mL bolus every 30 minutes. Ultrasound guidance and dosed with 10-20 mL of lidocaine 2% or bupivacaine 0.25%. Femoral nerve catheters were placed under Prior to February 2018, femoral nerve catheters were part of the postoperative pain management regimen. Regional analgesia techniques are usually performed prior to surgery. Our approach to postoperative regional analgesia has evolved over the past few years as an increased emphasis has been placed on efforts Generally, a waning spinal anesthetic is manifested by obvious patient discomfort, tachycardia, or hypertension.Ī regional analgesia technique is a consistent component of the multimodal postoperative pain management strategy. The epidural may be dosed with 2% lidocaine or 0.25% bupivacaineĪs needed in doses of 3-5 mL to extend the duration of neuraxial anesthesia. An epidural remains in place in case an extended duration of anesthesia is required to complete the surgical procedure. Isobaric bupivacaine is the typical dose for the spinal component. For the combined spinal-epidural, 2-3 mL of 0.5% All patients have the option of receiving either combined spinal-epidural or general anesthesia as the primary anesthetic. Regional anesthesia procedures are generally performed in the preoperative area. Patients with any evidence of liver disease do not receive acetaminophen.įigure 1: Adductor canal block with the needle lateral to the femoral artery underneath the sartorius muscle. Celecoxib is not given to patients with a history of renal insufficiency (creatinine > 1.5) or allergy (sulfa or celecoxib).

In the preoperative holdingĪrea, patients receive an oral pain pack which consists of acetaminophen 1000 mg, celecoxib 200 mg, and gabapentin 400 mg. This oral solution is withheld in the setting of delayed gastric emptying or symptomatic reflux disease. Two hours prior to presenting to the operating room, patients are asked to drink a 300 mL complex carbohydrate solution. It is therefore imperative that any perioperative analgesic pathway is able to provide safe, effective, and These comorbidities can frequently result in a prolonged recovery period following surgery.
Of Illinois Hospital are obese or morbidly obese. In addition, 61% of patients presenting for TKA at the University TKA patients frequently present with significant comorbidities, such as diabetes (27%), hypertension (73%), pulmonary disease (21%), congestive heart failure (4%), and other chronic conditions. We have sought to create a regimen for postoperative analgesia that provides excellent pain control while simultaneously decreasing lower extremity weakness, diminishing the risk of postoperative falls, and meeting the goals of physical therapy. In this article, we will describe our current total joint As with many institutions, we have sought to create a regimen for postoperativeĪnalgesia that provides excellent pain control while simultaneously decreasing lower extremity weakness, diminishing the risk of postoperative falls, and meeting the goals of physical therapy. Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is a common surgery for advanced knee arthritis, and the procedure has been growing in frequency, particularly in communities with aging populations.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
